You’ve heard of the Bro Code and seen all the different Bro Tips, right? Well, OCC is abiding by the Pro Code and we’d like to start sharing some of our Protips™ that everyone in the structured cabling business should know about!
As network infrastructures grow to encompass increased building automation, IP devices, and wireless access points, the need for communications components that meet these demands also grows. OCC’s Cat 6A Shielded Solution can provide 10-Gig performance and mitigate the EMI issues that come with running large amounts of cables for higher bandwidth applications. Our high performance cabling and connectivity products ensure the data within the cable will be protected from EMI, resulting in higher speeds and better data transmission.
Features & Benefits:
This week’s blog comes from Jamey Calloway, Product Management Specialist
The growth of wireless access points and other IP-enable devices, such as surveillance cameras and building automation devices has created a need to change the way typical horizontal links and channels are configured for these applications. Devices such as wireless access points mounted in non-traditional locations (in the ceiling or high up on the wall) are not attached to the network using standard faceplate/jack and patch cord. The traditional method is being replaced with direct attachment where the horizontal cable is terminated with a field installable plug and then plugged directly into the equipment (See Figure 1).
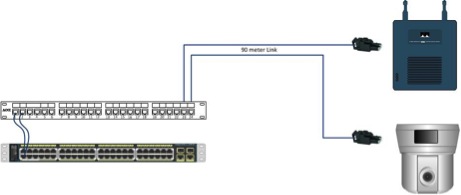
Currently, installers in the field are utilizing modular plugs that are intended for patch cord construction to terminate Cat5e and Cat6 cabling. This practice is difficult, time consuming, yields unpredictable performance results and is not recommended by the TIA-568 standards. Also, these plugs do not accommodate the larger conductors utilized in Cat6A cabling. The increasing data rates of wireless access points and other devices now require a Cat6A cabling link to support 10G Ethernet. The latest IEEE 802.11ac wireless standard under development supports a theoretical data throughput of 6.9Gbps.
Clearly, the best method is to utilize Field Terminable Plugs designed specifically for field installation and to support Cat5e, 6, and 6A cabling infrastructure. These plugs feature a robust design for field installation, require no specialized tooling and the termination procedures are very similar to many tool-less modular jacks in the market. Due to growing demand and emergence of field installable plugs, industry standards such as TIA-862-A, Building Automation Systems Cabling Standard and BICSI-005D, Electronic Safety and Security (ESS) System Design now recognize the direct attach method of termination.
As the global PC market continues to decline (3.5% global market decline in 2012) and wireless-only devices, such as tablets (expected to grow 70% in 2013) and smart phones continue to grow, the demand for direct attached connectivity will also expand in order to support the wireless infrastructure for these devices. It is undeniable that the future enterprise networks will be a combination of wired and wireless connectivity. It is imperative that industry standards and practices keep pace with a changing market.
To keep pace, OCC plans to release a Field Terminable Plug this coming fall 2013. While these products are still in development, it is important to recognize the growing demand for field terminable hardware and the applications where our pending product line will fit.
Energy predictions at the turn of the century were dire. The world was looking at a future of limited fossil fuels and an economy where gas would be $10.00 a gallon or higher in the United States. By now, cars and trucks were supposed to be running on fuel made from plant material, restaurant waste or hydrogen batteries that never need recharging. Electricity was supposed to be generated from solar panels, or wind generated turbines or neighborhood hydrogen power packs. Fossil fuels were to be extinct, a thing of the past. However, oil and gas companies have used technology to find oil and natural gas reserves so large that worries about running out have all but disappeared. The result of this technology is an abundance of fossil fuels yet to be tapped. Reports estimate that the United States is on track to become one of the world’s largest producer of oil and gas in a few years. Yet, these reserves aren’t limited to Texas, North Dakota and the deep waters (30,000 to 35,000 feet) of the Gulf of Mexico. Overseas, enormous reserves have been found in the deep waters of the North Sea, East and West Africa, Australia, South America and the Mediterranean.
While most view oil and gas rigs as big dumb chunks of steel with “fly by the seat of their pants” rough necks and roustabouts running everything, the amount of computing and data acquisition power aboard as well as the education level of the staff can be shocking. New geological imaging technologies let drillers find oil and gas trapped miles underground and thousands of feet undersea. Land Based oil rigs “walk” from one drill site to the next. And engineers located in Houston, Texas use remote-controlled equipment to drill for oil and gas in locations around the world.
The result of these new technologies has increased the demand for high speed data and increased bandwidth in automation, control and safety systems within the oil and gas markets. During OTC 2013 in Houston, Texas, a technical session was dedicated to the use and demands of fiber optic cable to support these new oil and gas technologies. During this session, white papers were submitted and supported by personnel from Shell, Chevron, Exxon/Mobil, BP, Schlumberger, Baker Hughes, Halliburton and others. The applications for fiber optic cable and harsh environment connectivity were widespread and diverse including:
The data demands of the oil and gas industry will continue to grow due to the increasing requirements to drill deeper wells in deeper water and longer horizontal drill runs while protecting personnel, the environment and equipment. OCC has products specifically designed for many of these types of 
The oil and gas industry has seen explosive growth in the technology they implore to find, drill, extract, and process these fossil fuels; which makes for a multitude of opportunities for OCC products. If you have questions about specific applications or products to meet the oil and gas industry, please contact us today for assistance!
OCC’s line of tactical fiber optic cables for deployable applications has always provided the most rugged and flexible method to deploy fiber over harsh terrain where a typical fixed cable installation is not possible. The polyurethane jacket on our deployable cables provides resistance to crush, impact, tear, and abrasion, and the cables provide excellent tensile strength. And because of their superior flexibility, deployable cables lie flat on the ground, retaining less reel memory when being deployed. Deployable composite copper/fiber cables provide an added level of versatility because they allow the user to supply low voltage power to devices that are connected by fiber.
OCC supplies composite deployable cables in standard configurations with up to 4 copper conductors, 18 to 12 gauge, which makes them ideal to pair with harsh environment connectivity solutions that offer copper and fiber connection. MHC-II connectors offer up to 8 copper and fiber connections while F-Link connectors can allow up to 33 copper and fiber connections. Customers in various markets are currently purchasing deployable composite cables and assemblies and using them in a number of applications. Some of these applications include:
OCC is ready to assist you in identifying the right deployable composite solution for your specific applications. Please contact your Sales Rep for assistance any time.